5 Tips for Maintaining Physical and Mental Health in the Elderly
Who are the elderly? what age are they considered as elderly?
In Thailand, the elderly are defined as individuals who are 60 years old and above. Additionally, the elderly are further categorized into three groups based on age:
- Early elderly: individuals aged between 60 and 69 years old
- Middle-aged elderly: individuals aged between 70 and 79 years old
- Late elderly: individuals aged 80 years old and above.
The health risks and hazards for the elderly population.
As individuals age, the health risks and various diseases become more complex and pronounced. Particularly if they have had a history of working hard and neglecting their health in the past, they may not have devoted much time to self-care. Some may have engaged in activities such as heavy alcohol consumption, smoking, or other risky behaviors. As they pass the age of 60, the consequences of these activities can increase health risks and susceptibility to diseases. Common health risks and diseases among the elderly population include, but are not limited to,
- Symptoms related to bone diseases, resulting from decreased efficiency in the body’s calcium absorption process to strengthen bones, may decrease effectiveness. This may lead to weakened bones in elderly individuals, increasing the risk of osteoporosis or easy bone fractures.
- Symptoms related to eye diseases arise from prolonged use of eyes, especially in today’s era where televisions, computers, smartphones, tablets, and other technological devices emit harmful radiation or have detrimental effects on eyesight. This may result in increased strain on the eyes, leading to rapid deterioration of the lenses or vision. Common eye conditions among the elderly may include cataracts, glaucoma, optic nerve degeneration, or macular degeneration.
- Symptoms related to memory and hearing loss diseases result from the declining efficiency of bodily functions as one age without realizing it. If elderly individuals have not maintained their physical health over time, they may experience problems such as ringing ears, deafness, difficulty hearing certain frequencies, or early signs of confusion and forgetfulness. If these symptoms worsen, it may lead to conditions such as dementia, disorientation, or difficulty recalling certain past events.
- Symptoms related to gastrointestinal diseases, resulting from the declining efficiency of the body’s normal digestive processes. This may make it harder for elderly individuals to control their bowel movements, or they may begin to notice symptoms such as frequent bloating, feverishness, or abnormal digestive functions. When seeking medical advice, doctors may recommend that elderly individuals consume easily chewable and digestible foods to accommodate the declining efficiency of their digestive systems.
- Symptoms related to mental health may arise from years of strenuous work, leading to accumulated stress that may cause elderly individuals to experience insomnia, anxiety, fatigue, or, in some cases, severe depression.
- Symptoms arising from weakened immune responses may result in elderly individuals experiencing symptoms such as colds, fevers, body aches, allergies, rashes, or other conditions because their immune systems cannot function normally.
These are just examples of health risks and diseases commonly encountered among the elderly. Certainly, some of these conditions cannot be avoided as one age. However, some of these conditions can be mitigated or even prevented if we take proactive steps to care for our health from the beginning. By practicing preventive healthcare, we may be able to alleviate or avoid severe health issues in the future.
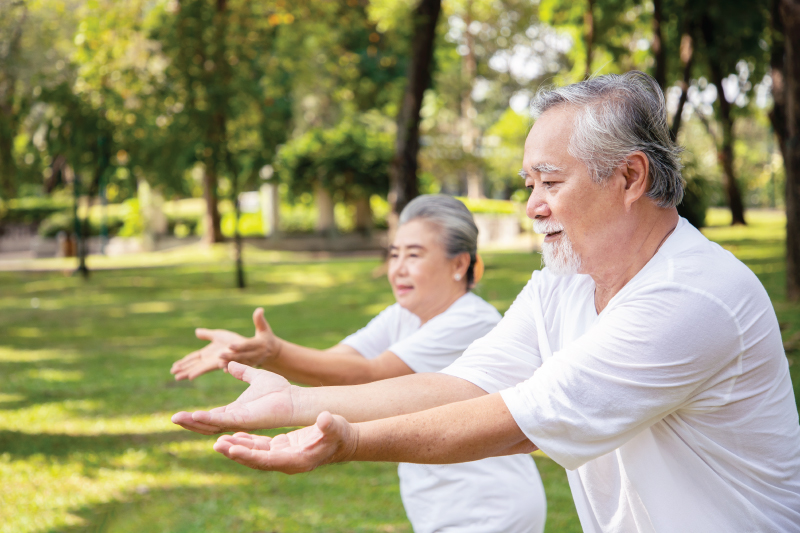

5 Tips for Maintaining Mental Health in the Elderly
- Consuming a balanced diet from all five food groups, with a variety of nutrients and vitamins essential for the body’s needs.
- Regular exercise to strengthen various muscles in the body.
- Regular visits to the doctor for health check-ups and screenings for underlying health conditions that may not yet show symptoms, to enable timely prevention or treatment.
- Receiving necessary vaccinations against various diseases is particularly important for the elderly who may be at higher risk and whose bodies may not produce sufficient immunity against these diseases.
- Engaging in simple activities or hobbies to stimulate the brain, memory, and necessary skills, helps to prevent or reduce cognitive decline and other brain-related issues.
5 Tips for Maintaining Physical Health in the Elderly
- Creating a supportive environment conducive to the mental well-being of the elderly involves caregivers or family members paying attention to various aspects of their surroundings. This includes maintaining cleanliness, fostering a positive social atmosphere, and ensuring that the elderly are not exposed to stressful information. Additionally, providing them with love and care from the family is essential.
- Understanding the emotional state of the elderly is crucial, as many may experience stress from their life experiences. This stress can lead to emotional fluctuations, anxiety, and abnormal behavior as they age. Therefore, family members need to understand and empathize with their elderly loved ones.
- Helping to alleviate stress in the elderly is important to prevent them from becoming anxious or experiencing mood swings. Engaging them in activities they enjoy, such as hobbies, visits to temples, dancing, music, or light sports, can help them relax and reduce stress. These activities can also improve physical health, making their bodies stronger and more resilient.
- Supporting the social integration of the elderly into various age groups is essential. Bridging the gap between generations is crucial in today’s society. Educating the elderly about the perspectives and developmental concepts of younger generations or societal groups can help them have a more diverse range of friends. Understanding society better and feeling less isolated can prevent problems such as withdrawal and loneliness, which can lead to stress, emotional instability, and other health issues.
- Showing respect and understanding for the elderly, listening to their concerns, and providing them with meaningful advice are vital aspects of caregiving. Many elderly individuals may not be working or able to care for themselves independently, making it crucial for caregivers and close relatives to be attentive and supportive.
Therefore, it’s not surprising that many elderly individuals often feel marginalized, worried about their children and grandchildren, and may perceive themselves as losing value within the family structure. Not being relied upon or considered the pillar of the family can significantly impact the emotional well-being of the elderly. Therefore, close family members need to understand, listen to, respect, and provide intimate advice to the elderly.
Summary:
In summary, The majority of Thai families typically have at least one or two elderly members. Maintaining the elderly requires attention to both their physical and mental well-being, similar to caring for infants or young children. As the body’s functions decline with age, various caregiving abilities may also diminish.
Therefore, caregivers must pay attention to details, both in terms of visible physical health and the need for mental health care, as the elderly may rely on observation. With advancements in health technology, caregiving for the elderly has become more effective in reducing various health risks through proper nutrition, exercise, and immune support. This helps maintain normal bodily functions, and delays or prevents health problems caused by weakened immunity or nutritional deficiencies. Additionally, modern health science offers a variety of products to address the specific healthcare needs of elderly individuals in each stage of aging.